Is Sugar Addictive? A Closer Look at Sugar Cravings
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among nutritionists and health experts. While sugar isn’t classified as an addictive substance in the same way as alcohol or nicotine, many individuals experience cravings that mirror addiction-like behaviors linked to sugar consumption. These cravings can lead to compulsive eating and, when attempting to reduce sugar intake, withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, anxiety, and dizziness may occur. Understanding the health effects of sugar and recognizing the patterns of sugar addiction is crucial in promoting healthier eating habits and reducing excessive sugar intake.
When discussing sugar and its impact on our health, it’s essential to consider terms like sweetener dependency or excessive sweetener desire. People often grapple with powerful urges to consume sugary foods, which can resemble the intense cravings seen in substance dependencies. The prevalence of highly processed foods loaded with sugar contributes to these cravings, leading many to question their relationship with sweeteners. Moreover, the withdrawal symptoms that come from cutting back on sugar can be unsettling, echoing the experiences associated with the cessation of more traditionally addictive substances. Recognizing the fine line between enjoyable sweet consumption and harmful sugar addiction is vital for maintaining overall wellness.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a heavily debated topic in nutrition science. Many individuals find themselves craving sugar and experiencing intense urges for sugary foods, which can be likened to addictive behaviors seen with substances such as alcohol or nicotine. However, according to experts, sugar is not classified as an addictive substance based on established clinical criteria. Instead, it exhibits qualities that can lead to compulsive eating and increased cravings, especially from highly palatable, ultra-processed foods.
The health effects of sugar consumption extend beyond just cravings. While it is important to recognize that we need some sugar in our diets for energy, the average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily. This excessive intake can lead to health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. It’s crucial for individuals to monitor their sugar intake, as the way sugar is incorporated into our diets can create patterns of habitual consumption that are difficult to break.
Is Sugar Truly Addictive? Debunking Myths
When discussing whether sugar is addictive, it’s essential to examine the physiological and psychological effects of sugar. While sugar can trigger cravings similar to those caused by addictive substances, the withdrawal symptoms associated with stopping sugar consumption, such as headaches and anxiety, are generally mild compared to those experienced with drugs like nicotine or alcohol. This spectrum of addiction makes it challenging to classify sugar within the standard definitions of addiction.
The distinction between necessary nutrients and addictive substances is crucial in this discussion. Sugar is found naturally in fruits, vegetables, and dairy, making it an essential energy source for our bodies. It’s the added sugars in processed foods that typically lead to excessive consumption and potential health risks. Moderation is key, and re-evaluating our sugar habits can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms without eliminating sugar entirely from our diets.
Sugar Cravings: Causes and Solutions
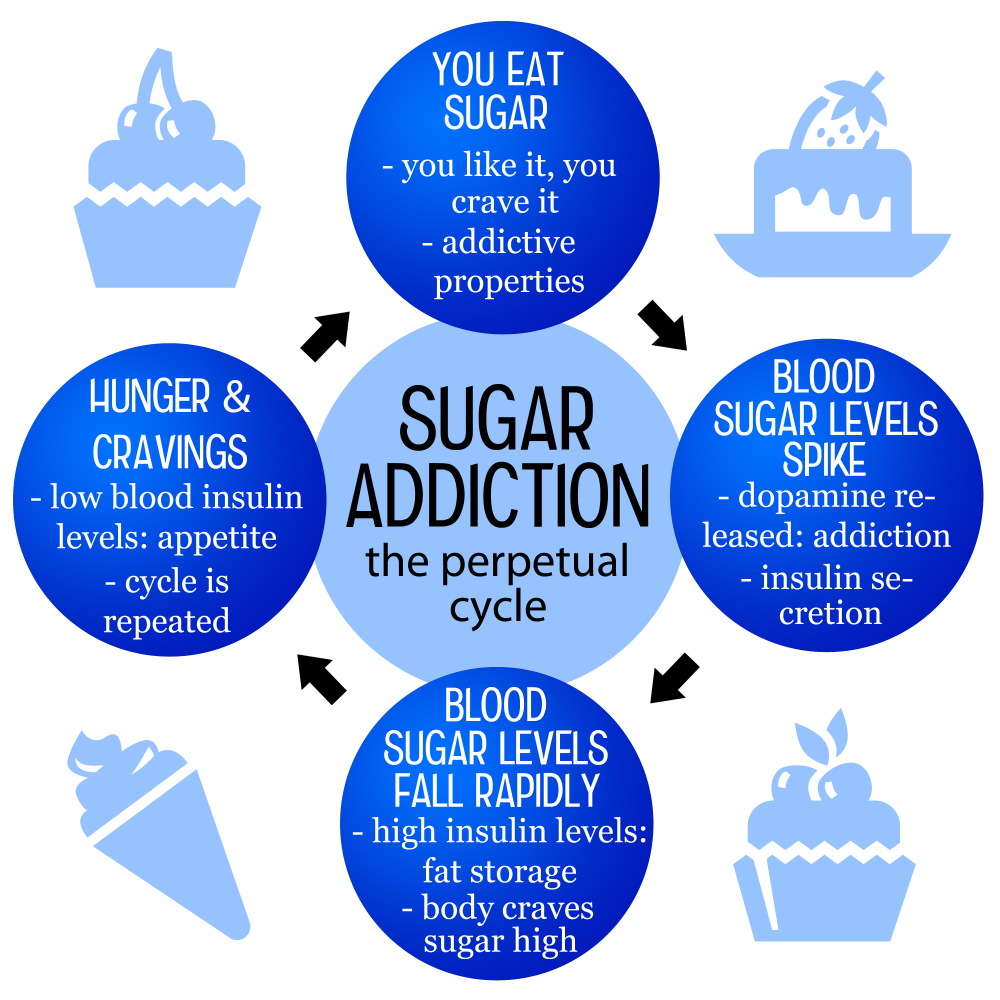
Craving sugar is a common experience, fueled by the high accessibility of sweet foods in our diets. These cravings often stem from the hedonic pleasure derived from consuming sweet flavors, influenced by both psychological factors and neurobiological responses. When we consume sugar, our brain releases dopamine, the ‘feel-good’ neurotransmitter, which reinforces the desire to seek out sugary foods again. Understanding this connection can empower individuals to manage their cravings more effectively.
To combat sugar cravings, experts recommend strategies such as gradually reducing sugar intake rather than eliminating it abruptly. This approach helps mitigate withdrawal symptoms and allows the body to adjust to lower sugar levels without triggering intense cravings. Additionally, incorporating whole, unprocessed foods into the diet can provide natural sweetness while promoting overall health, ultimately balancing the enjoyment of sweetness with nutritional needs.
The Health Effects of Excessive Sugar Consumption
The health effects of excessive sugar consumption are profound and concerning. High sugar intake is linked to numerous health problems, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugars to prevent these detrimental health outcomes. By recognizing the signs of excessive sugar consumption in our diets and understanding its long-term effects, individuals can make informed dietary choices.
Moreover, the pervasive nature of sugar in many processed foods makes it easy to exceed the recommended daily limits without realizing it. Keeping track of sugar intake through food labels and being mindful of hidden sugars in snacks can be effective strategies. By prioritizing a balanced diet that limits added sugars while enjoying the natural sweetness found in whole foods, one can support better health outcomes.
Sugar Withdrawal Symptoms: What to Expect
When individuals significantly reduce their sugar intake, they may experience withdrawal symptoms similar to those seen with addictive substances. Symptoms include headaches, mood swings, fatigue, and irritability, which can make the process of cutting back on sugar particularly challenging. Understanding these symptoms can help individuals prepare and strategize for this adjustment period in their diets.
It’s important to note that these sugar withdrawal symptoms, while uncomfortable, typically diminish over time as the body adjusts to lower sugar levels. Staying hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet, and seeking support during this transitional phase can be beneficial. Gradually decreasing sugar intake instead of eliminating it entirely can also lessen the severity and duration of these symptoms, providing a more manageable path towards a healthier lifestyle.
Balancing Sugar in Our Diets: The Key to Health
Finding a balance with sugar in our diets is crucial for maintaining overall health. Sugar, when consumed in moderation, can enhance flavors and provide energy. The key is understanding what constitutes a moderate amount and recognizing the difference between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods that contain natural sugars, individuals can satisfy their sweet tooth without compromising their health.
Establishing healthy eating patterns that include occasional indulgences can also prevent feelings of deprivation, potentially reducing the risk of binge eating on sugary foods. Education about sugar content in various foods and mindfulness around eating can equip individuals with the tools needed to enjoy sugar while minimizing negative health outcomes. It’s all about moderation and making informed choices that align with our nutritional needs.
The Importance of Reading Food Labels for Sugar Content
Reading food labels is an essential practice for anyone looking to manage their sugar intake effectively. Many products, even those marketed as healthy, can contain significant amounts of added sugars. By understanding how to decode these labels, consumers can make more informed choices that align with their health goals and avoid unnecessary sugar consumption.
Looking for terms such as high fructose corn syrup, cane sugar, or glucose on labels can help identify added sugars in products. Additionally, being aware of serving sizes is crucial, as what may seem like a low sugar item can become problematic when consumed in larger portions. Enhancing label literacy among consumers is vital in the fight against excessive sugar consumption and subsequent health problems.
Curbing Sugar Cravings: Healthy Alternatives
One effective strategy for managing sugar cravings is to explore healthy alternatives that satisfy the desire for sweetness without resorting to high-sugar options. This could involve utilizing natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup, which offer flavor without the same health risks associated with refined sugars. Additionally, incorporating fruits into meals and snacks provides natural sugars along with beneficial nutrients and fiber.
Moreover, experimenting with spices such as cinnamon or vanilla can enhance flavors in foods and beverages, providing satisfaction without adding significant sugar. Creating balance in the diet by replacing sugary snacks with nutrient-dense options like yogurt with fresh fruit or nut-based energy bars can effectively curb cravings while promoting better overall health.
The Psychological Impact of Sugar Addiction
The psychological impact of sugar addiction can be profound, affecting not only physical health but mental well-being as well. Individuals may find that their cravings for sugar interfere with their daily lives and emotional stability, leading to feelings of guilt or frustration. Addressing these issues may require a multi-faceted approach, considering both the physiological and psychological aspects of sugar consumption and potential addiction.
Counseling or support groups focused on nutrition and emotional eating can provide valuable resources for those struggling with sugar cravings. Cognitive-behavioral strategies can also help individuals reframe their perceptions of sugar and develop healthier relationships with food. By addressing the psychological components of sugar consumption, it is possible to mitigate cravings and promote a healthier lifestyle overall.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like nicotine or alcohol?
While sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like nicotine or alcohol. Research indicates that sugar can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms when reduced, but these effects are less severe than those associated with true addictive substances.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Health effects of sugar addiction can include increased cravings for sweet foods, habitual sugar consumption, and potential withdrawal symptoms such as headaches and anxiety. Additionally, excessive sugar consumption is linked to various health issues like obesity and type 2 diabetes.
How does sugar consumption lead to cravings?
Sugar consumption can create a cycle of cravings due to its palatable nature and prevalence in ultra-processed foods. These foods are often high in added sugars, making them addictive in taste, which can lead to habitual consumption and increased cravings over time.
What are common sugar withdrawal symptoms?
Common sugar withdrawal symptoms may include headaches, dizziness, anxiety, and mood swings. These symptoms can occur after suddenly reducing or eliminating sugar from the diet, as the body adjusts to lower sugar levels.
Can I gradually reduce sugar consumption to combat sugar addiction?
Yes, gradually reducing sugar consumption can help prevent withdrawal symptoms and make it easier to manage cravings. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons per day for men and 6 teaspoons for women.
Is it possible to eliminate sugar completely from my diet?
Completely eliminating sugar is challenging and may not be necessary since some sugars are naturally present in nutritious foods like fruits and whole grains. Moderation is key, and focusing on reducing added sugars while maintaining a balanced diet is preferred.
How can I manage sugar cravings effectively?
To manage sugar cravings effectively, consider eating a balanced diet rich in whole foods, drinking plenty of water, and being mindful of your sugar intake. Reading food labels and slowly reducing added sugars can also help curb cravings and promote healthier choices.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Cravings for Sugar | Cravings for sugar are real, but sugar is not officially classified as an addictive substance due to clinical criteria. |
| Comparison to Drugs | Unlike alcohol, nicotine, and opiates, the withdrawal symptoms from sugar are less severe, although they can exist (like headaches and anxiety). |
| Processed Foods | Ultra-processed foods high in added sugar can lead to increased cravings. Be mindful of sugar levels in diets. |
| Necessary Nutrient | Sugar is found in healthy foods like fruits and dairy. It is essential in moderation, unlike drugs that can be eliminated. |
| Consumption Recommendations | The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and less for children. |
| Gradual Reduction is Key | Going ‘cold turkey’ on sugar can backfire; gradual reduction is advised. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among nutrition experts. While sugar has some addictive qualities, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria that classify substances like alcohol and nicotine as truly addictive. Sugar contributes to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, primarily when consumed through ultra-processed foods. However, unlike drugs that can be eliminated entirely, sugar is inherently part of many nutritional foods necessary for health. Understanding how sugar fits into our diets and managing its consumption can lead to a healthier relationship with sweets.