Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.: Rising Concerns
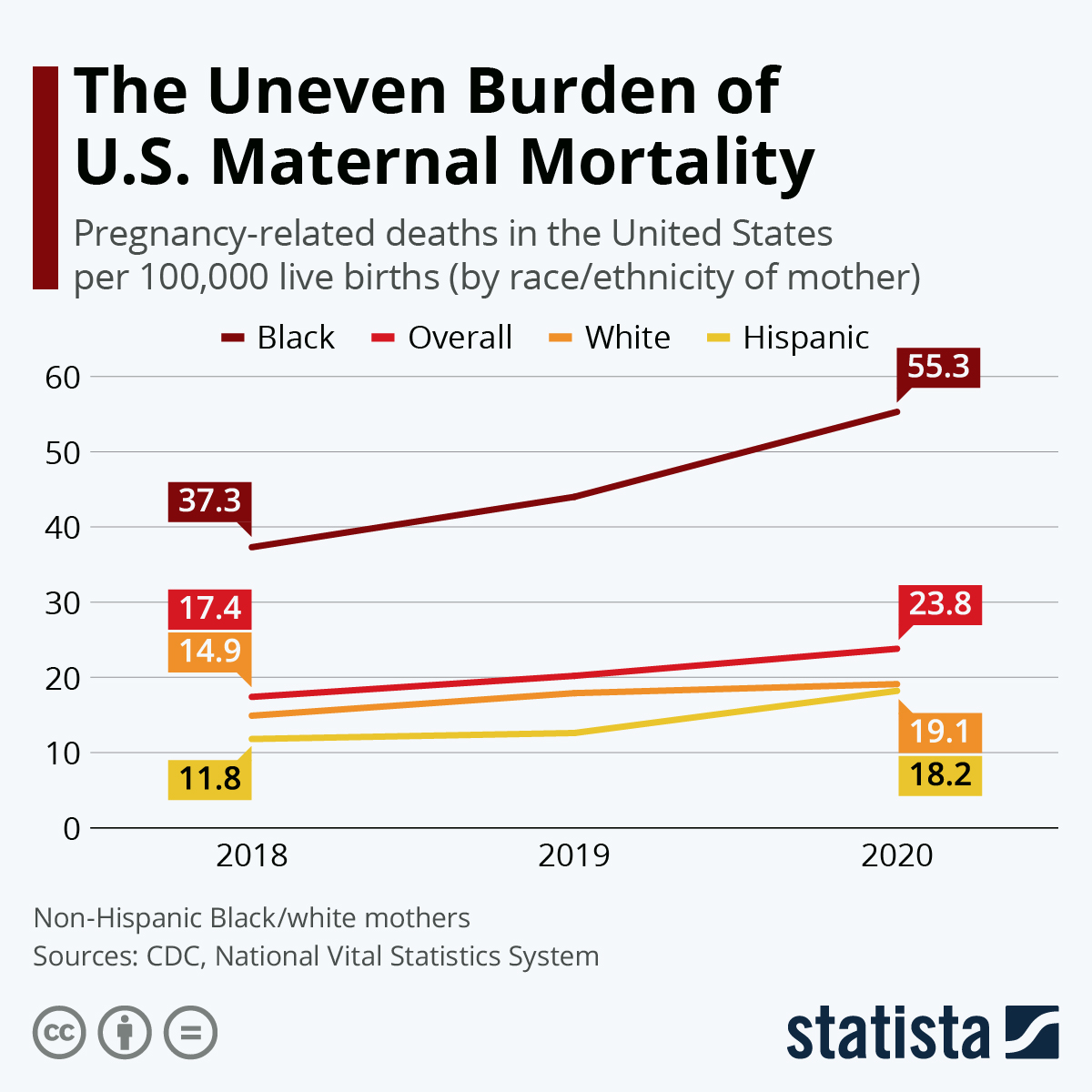
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. have become a critical issue, as the nation consistently reports one of the highest figures among high-income countries. Despite the alarming statistic that over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, progress remains sluggish. The disparity in maternal health outcomes is stark, revealing significant inequalities influenced by race, ethnicity, and geography. Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of these deaths, highlighting a pressing public health concern that demands urgent attention. Enhanced postpartum care and targeted interventions are essential to address the root causes, reduce high maternal mortality rates, and promote equity in maternal health across the country.
The rise in pregnancy-related deaths reflects a deeper crisis in maternal healthcare in the United States. Documenting the challenges associated with childbirth, researchers are increasingly focusing on understanding the factors contributing to maternal health disparities across various demographics. By examining healthcare access and the effects of chronic conditions during pregnancy, it’s evident that systemic changes are necessary to curtail the significant rate of motherhood-related fatalities. With cardiovascular disease now identified as a predominant factor, it becomes imperative to prioritize comprehensive care before, during, and after pregnancy. Health professionals and policymakers must shift their approach, ensuring that those at highest risk receive the support and resources they need for healthier outcomes.
Understanding Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. are alarmingly high, having increased steadily over the past few years. A recent study has highlighted that over 80 percent of these cases are preventable, indicating a significant gap in the healthcare system’s ability to manage and support women’s health during and after pregnancy. The nation has consistently reported the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with substantial variations in rates across different states and ethnic groups. This inconsistency raises urgent questions about access to quality healthcare and the effectiveness of existing maternal health policies.
The study conducted by NIH researchers revealed troubling disparities, particularly among racial and ethnic groups. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face nearly four times the risk of pregnancy-related deaths compared to their white counterparts. Such findings call for a reevaluation of health care accessibility and targeted interventions to address systemic issues in maternity care that disproportionately affect marginalized communities. Understanding the complexities behind these statistics is essential in developing approaches to reduce the overall mortality rates and enhance maternal health.
The Impact of Postpartum Care on Maternal Health
Postpartum care plays a crucial role in maternal health, particularly in preventing late maternal deaths, which now comprise nearly a third of pregnancy-related fatalities. Current healthcare systems often view postpartum recovery as a separate entity from the immediate care offered during pregnancy, which can lead to significant gaps in the support provided to new mothers. By recognizing postpartum care as a continuum that extends beyond the six weeks traditionally allocated, healthcare practitioners can better address ongoing health issues many women face after giving birth.
Innovative approaches to postpartum care are essential, especially given that many pregnancy-related fatalities stem from conditions exacerbated during this period. Continued monitoring for chronic conditions like hypertension and cardiovascular disease is necessary to ensure that women receive adequate support. These efforts can greatly improve health outcomes for mothers and prevent avoidable deaths, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive care that integrates both pregnancy and postpartum health.
Addressing Maternal Health Disparities Across Different Communities
Maternal health disparities remain a critical issue, with significant variations in pregnancy-related outcomes among different racial and ethnic groups. The findings from recent studies underscore the urgent need for targeted interventions that address these disparities, particularly for populations that have historically faced inequitable healthcare access. For instance, the staggering rates of maternal mortality among American Indian and Alaska Native women demand immediate policy action and innovative programs tailored to support their unique healthcare needs.
Healthcare systems must work to dismantle the biases and structural barriers that contribute to these disparities in maternal health. This includes not only increasing the availability of culturally competent care but also ensuring equitable access to prenatal and postpartum services. Addressing these disparities requires a multi-faceted approach that encompasses education, community support, and systemic change to create an inclusive healthcare environment where all women can expect to receive the care they deserve.
The Role of Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of pregnancy-related death in the U.S., highlighting a critical area of concern for maternal health. Recent studies indicate that over 20 percent of maternal deaths can be attributed to various cardiovascular conditions, including hypertensive disorders and peripartum cardiomyopathy. This shift in cause of death reflects a concerning trend, indicating that more women are entering pregnancy with preexisting health issues, underscoring the need for better screening and management of cardiovascular health during preconception and pregnancy.
The increasing prevalence of chronic health conditions like hypertension among younger women poses significant risks during pregnancy, pointing to the necessity of improving cardiovascular health education and intervention strategies. Healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring these women throughout pregnancy, ensuring that they receive comprehensive care that includes managing their cardiovascular risk factors effectively. Addressing the intersection of cardiac health and maternal care not only improves outcomes for mothers but also sets the stage for healthier futures for their children.
Improving Prenatal Care for Better Maternal Health Outcomes
Enhancing prenatal care is essential in reducing high maternal mortality rates in the U.S. Comprehensive prenatal care should include regular screenings, personalized management of risk factors, and education about pregnancy-related complications. Studies suggest that states with robust prenatal care programs show significantly lower maternal mortality rates. By implementing evidence-based practices and making prenatal care accessible to all women, healthcare systems can take substantial strides in preventing pregnancy-related deaths.
Moreover, it is imperative that healthcare providers prioritize continuous education on the signs of complications during pregnancy and ensure that women feel empowered to seek care when needed. Creating a supportive environment that encourages consistent and open communication between healthcare providers and expectant mothers can foster better understanding and management of maternal health. Ultimately, bolstering prenatal services will contribute directly to better outcomes, reducing disparities across different demographics, and saving lives.
The Importance of Comprehensive Maternal Health Policies
Effective maternal health policies are vital in addressing the rising maternal mortality rates and the disparities that persist across different communities. Policymakers must recognize that the healthcare system’s fragmentation often leaves many women without the essential support they need. By developing comprehensive policies that ensure access to quality prenatal and postpartum care for all women, the country can begin to make meaningful progress in improving maternal health outcomes.
Additionally, targeted efforts to fund maternal health programs that specifically address the needs of high-risk populations, including racial and ethnic minorities, are critical. These initiatives should involve collaboration between healthcare providers, community organizations, and policymakers to create sustainable changes that improve access, education, and support. By prioritizing maternal health in legislative agendas, we can work towards a future where all women have equitable access to care and fewer maternal lives are lost.
Innovative Solutions for Enhancing Maternal Health Services
Innovative solutions are necessary for enhancing maternal health services and addressing the dire statistics surrounding pregnancy-related deaths. Technology plays a pivotal role in this transformation, from telehealth consultations that increase access to specialized care for women in rural areas, to mobile health applications designed to monitor maternal health conditions in real-time. Integrating these tools into current healthcare systems can provide timely interventions and education to expectant and postpartum mothers, thereby improving outcomes significantly.
Moreover, fostering partnerships between healthcare organizations and community-based initiatives can lead to innovative health programs that address specific needs within various populations. For example, creating culturally tailored education and resource programs focused on maternal health can help bridge the gaps that exist in healthcare access. By continuously seeking and implementing innovative strategies, we can work towards a comprehensive and equitable maternal health system that effectively reduces mortality rates.
Significance of Tracking Maternal Deaths for Policy Change
The establishment of a national system for tracking maternal deaths in the U.S. is a significant step towards understanding and ultimately decreasing the high maternal mortality rates. Since implementing the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates, healthcare authorities can now obtain valuable data that shed light on the causes and circumstances surrounding pregnancy-related deaths. This data is essential for formulating informed policies and interventions that can specifically target areas of concern in maternal health.
Moreover, consistent tracking allows for real-time monitoring of maternal health trends, enabling policymakers and healthcare professionals to respond quickly to emerging issues. By investing in robust surveillance systems, we can ensure ongoing visibility into maternal health outcomes, prompting necessary changes in public health infrastructure and funding allocations. The ultimate goal is to create a system where data informs practice, leading to tangible improvements in health outcomes for mothers across the nation.
The Need for Enhanced Public Health Infrastructure
The rising trend in maternal mortality rates highlights an urgent need for enhanced public health infrastructure focused on maternal health. As studies indicate a worrying increase in pregnancy-related deaths, particularly among marginalized communities, strategic investments in healthcare resources are more critical than ever. Strengthening the overall public health framework will facilitate better care coordination and resource allocation, ultimately leading to healthier outcomes for mothers and babies.
Moreover, as evidenced by the findings from recent maternal mortality studies, it is crucial to prioritize funding for research and community health initiatives that address the unique challenges women face during pregnancy and postpartum recovery. By ensuring that public health remains a priority in governmental budgets and policy discussions, we can effectively work towards mitigating the alarming rates of maternal mortality and improving health equity across diverse populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current maternal mortality rates in the U.S. compared to other high-income countries?
The maternal mortality rates in the U.S. are alarmingly high, with the nation leading among high-income countries. Data from 2022 indicated 32.6 pregnancy-related deaths per 100,000 live births, indicating a troubling increase from 25.3 in 2018. This emphasizes a critical need for enhanced maternal health policies and comprehensive postpartum care.
What factors contribute to high maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
High maternal mortality rates in the U.S. can be attributed to a combination of factors. These include a fragmented healthcare system, inequitable access to care, disparities in maternal health across racial and ethnic groups, as well as an increase in chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease among women of reproductive age.
What are the significant racial disparities observed in maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Racial disparities in maternal mortality rates are stark in the U.S. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience a rate of 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births, compared to 27.6 for white women and 76.9 for non-Hispanic Black women. This underscores the need for targeted interventions to address maternal health disparities.
How do cardiovascular diseases affect maternal mortality rates during pregnancy?
Cardiovascular diseases have emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for over 20% of such deaths. Conditions such as hypertension, pre-eclampsia, and cardiac arrest are affecting younger women, contributing significantly to the overall high maternal mortality rates.
What role does postpartum care play in addressing maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Postpartum care is crucial in addressing maternal mortality rates, especially since nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days to a year after childbirth. Enhancing postpartum healthcare and viewing recovery as a continuum can potentially reduce these preventable deaths and improve maternal health outcomes.
Why is it important to track late maternal deaths when analyzing maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Tracking late maternal deaths, which occur from 42 days to one year postpartum, is vital because it highlights the ongoing health challenges women face after childbirth. This aspect of maternal mortality is often overlooked but is essential for developing comprehensive solutions and ensuring robust maternal healthcare throughout the entire postpartum period.
What needs to be done to improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S.?
To improve maternal health outcomes, the U.S. must invest in public health infrastructure, enhance access to quality maternal care, and address disparities in healthcare policies across states. Continuous investment in both prenatal and extended postpartum care is essential to reduce the high rates of pregnancy-related deaths.
How do maternal health disparities impact pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Maternal health disparities significantly affect pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., as evidenced by the differing mortality rates among racial and ethnic groups. Addressing underlying issues of biased healthcare practices, improving access to resources, and promoting equity in maternal care is critical for reducing these disparities.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Maternal Mortality Rates | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, rising from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022. |
| Disparities | Significant racial disparities exist: American Indian/Alaska Native women face the highest rates (106.3), compared to white women (27.6) and non-Hispanic Black women (76.9). Variability by state ranges from 18.5 to 59.7 deaths. |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths are due to cardiovascular disease, indicating a shift from hemorrhage as the leading cause. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly a third of deaths occur between 42 days and 1 year post-pregnancy, highlighting the need for extended postpartum care. |
| Public Health Infrastructure | There’s a call for improved public health investment to maintain tracking systems and enhance maternal health care systems. |
Summary
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. have reached alarming heights, with an increase from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022, highlighting a pressing public health crisis. Despite over 80% of these deaths being preventable, systemic issues such as healthcare disparities, chronic diseases among younger populations, and inadequate postpartum care persist. Disparities based on race and state further worsen the situation, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest mortality rates. To combat this, it is crucial to invest in public health infrastructure, improve prenatal and postpartum care, and address the root causes of these disparities to protect maternal health and prevent further loss of life.