Maternal Mortality Rates: The Rising Crisis in the U.S.
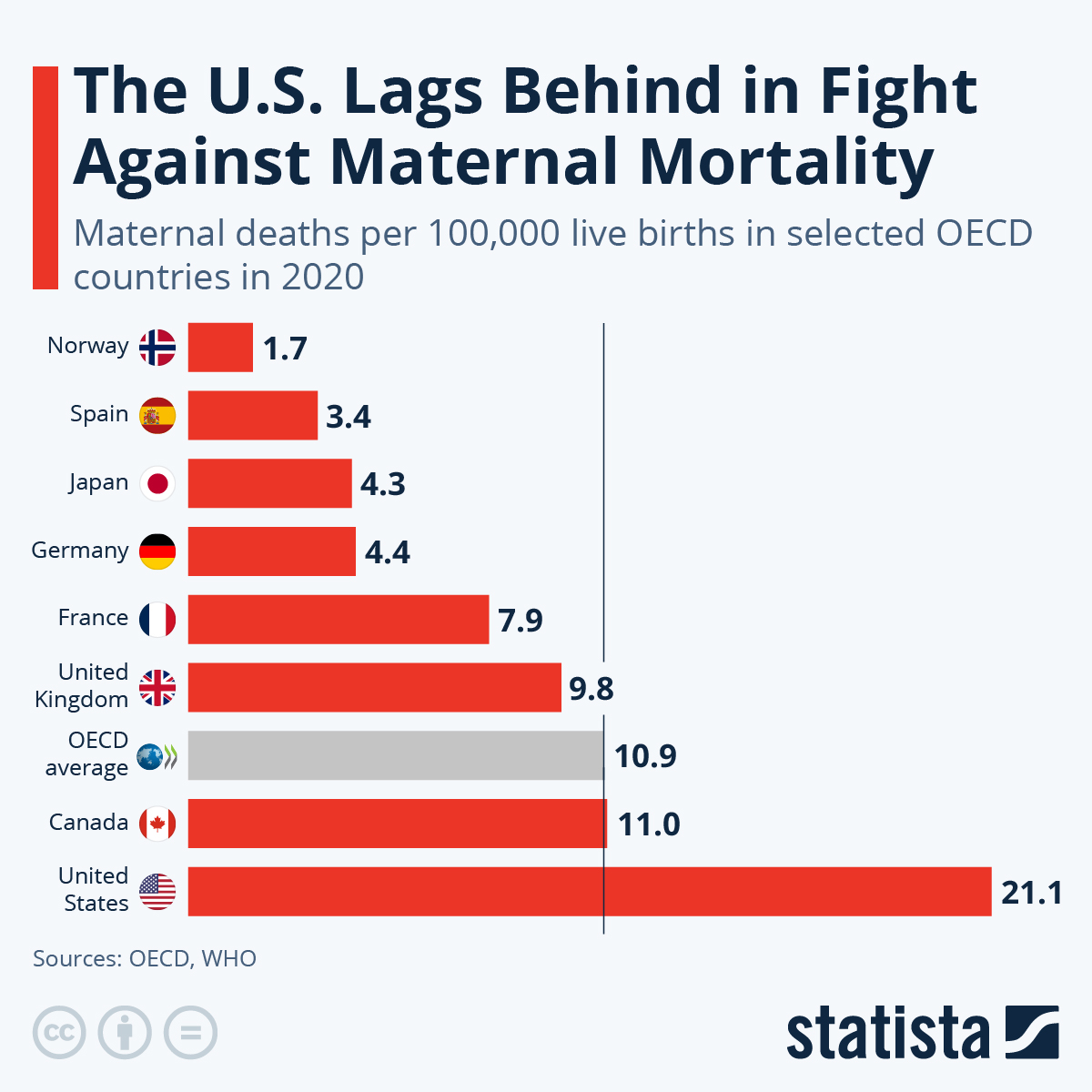
Maternal mortality rates have emerged as a pivotal concern in the U.S., where statistics indicate that over 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. Shockingly, the nation consistently ranks at the top of maternal mortality among high-income countries, with rates that have risen steadily between 2018 and 2022. The disparities rooted in state, race, and ethnicity further complicate this troubling picture, showcasing significant variations in fatalities among different demographics. Factors ranging from inadequate postpartum care to cardiovascular disease during pregnancy exacerbate the plight of expectant mothers. As researchers urge a reevaluation of prenatal and postpartum healthcare systems, it becomes clear that addressing these disparities is not only a health imperative but a moral one as well.
When examining the alarming trends surrounding pregnancy-related fatalities, the term “maternal health crises” comes to mind, echoing broader themes of maternity-related deaths and healthcare inefficiencies. Despite the advancements in medical science, the prevalence of preventable pregnancy deaths remains distressingly high, paving the way for discussions on maternal wellness gaps. Many women face systemic barriers during their perinatal journey, highlighting the urgent need for improved standards of postpartum care and more accessible healthcare solutions. Additionally, the ongoing risk of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease during pregnancy further complicates the landscape, demanding immediate attention. As we delve into this pressing issue, it is crucial to advocate for holistic strategies that prioritize women’s health throughout the entire reproductive continuum.
Understanding Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
Maternal mortality rates in the United States remain unacceptably high, particularly when compared to other affluent nations. Over the past decades, the U.S. has consistently topped the list of high-income countries with the highest maternal mortality rates, with figures indicating significant increases since 2018. The rise in pregnancy-related deaths illustrates a critical crisis in maternal health, driven by factors such as inadequate access to prenatal care, systemic inequities in healthcare delivery, and the ongoing impact of chronic health conditions among pregnant individuals.
Moreover, the alarming statistics uncover the hidden disparities that exist within various demographics. American Indian, Alaska Native, and non-Hispanic Black women face disproportionately higher risks of maternal mortality compared to their white counterparts. These discrepancies serve to highlight the urgent need for targeted interventions and the reevaluation of health policies affecting marginalized communities. Addressing maternal mortality rates is pivotal not only for improving health outcomes but also for ensuring equitable access to safe and effective prenatal and postpartum care.
The Link Between Preventable Pregnancy Deaths and Healthcare Access
A staggering 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are classified as preventable, emphasizing the urgent need for enhanced access to quality healthcare throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period. Many preventable deaths can be attributed to a lack of appropriate prenatal services and insufficient postpartum care, which are essential for monitoring and addressing health complications. By prioritizing comprehensive maternal healthcare, the U.S. can significantly reduce preventable deaths and improve health outcomes for mothers and their babies.
Moreover, the fragmentation of healthcare services poses a formidable barrier to effective maternal health management. In many regions, especially in rural areas, maternity care deserts exacerbate the challenges faced by expectant mothers, leading to a failure to receive timely interventions and ongoing support. To combat this issue, there is an urgent need to develop innovative healthcare frameworks that expand access to quality prenatal and postpartum care, thereby addressing the systemic issues that contribute to preventable pregnancy-related deaths.
Racial Disparities in Maternal Health Outcomes
Racial disparities in maternal health outcomes continue to pose a significant challenge within the United States. The stark contrasts in maternal mortality rates among different racial and ethnic groups underscore the systemic inequities that persist in the healthcare system. Factors such as discrimination, socioeconomic status, and differing access to healthcare resources contribute to elevated risks for women of color. For example, American Indian and Alaska Native women face mortality rates nearly four times higher than white women, highlighting the critical need for comprehensive policy reforms.
Addressing these racial disparities requires a multifaceted approach that includes not only healthcare delivery improvements but also broader societal changes. Community engagement, culturally competent care, and the empowerment of marginalized voices within the healthcare discourse are essential components of a solution. Programs aimed at reducing bias and improving access to culturally sensitive care can pave the way for equitable health outcomes, ensuring that all women have the opportunity for safe pregnancies and healthy births.
The Impact of Cardiovascular Disease on Maternal Health
Cardiovascular disease is emerging as the leading cause of maternal mortality, accounting for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. The rising prevalence of chronic conditions such as hypertension among younger women dramatically influences these statistics. As cardiovascular complications become more common, particularly among women aged 25 to 39, it is crucial that healthcare providers screen for and manage these risks effectively before and during pregnancy.
This shift in the leading causes of maternal mortality necessitates a reevaluation of prenatal and postpartum care strategies. By integrating cardiovascular health assessments into routine prenatal visits, healthcare providers can identify at-risk individuals earlier and implement necessary interventions. Furthermore, the focus should extend beyond the immediate postpartum period, emphasizing the continuum of care required to monitor and address cardiovascular health in mothers for up to a year after delivery.
Addressing Maternal Health Disparities Across States
Significant variations in state-level maternal mortality rates reveal deep-rooted discrepancies in healthcare access and quality. For example, the research indicates that a substantial number of pregnancy-related deaths could have been prevented if states with lower mortality rates could serve as models for others. This underscores the critical need for a cohesive approach to maternal health policies that bridges the gaps between states and ensures that all women, regardless of where they live, receive adequate prenatal and postpartum care.
State-level policy interventions are key to addressing these disparities. By learning from successful programs and practices implemented in states like California, other regions can begin to enact evidence-based policies that prioritize maternal health. Invested efforts should focus on enhancing healthcare infrastructure, providing education on maternal health, and fostering local community engagement to cultivate an environment where maternal health disparities can be reduced.
Late Maternal Deaths: The Overlooked Crisis
Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and one year after delivery, account for a significant portion of maternal mortality yet are often overlooked in discussions surrounding maternal health. The failure to fully acknowledge this critical period reveals gaps in postpartum care systems, which are traditionally not designed to extend beyond the first six weeks after childbirth. This lack of coordinated long-term care can lead to preventable tragedies.
To rectify this oversight, healthcare systems must adopt a more inclusive definition of maternal care that addresses the postpartum period as a continuum rather than a distinct phase. By implementing follow-up care protocols that prioritize the health of mothers well beyond the initial postpartum weeks, healthcare providers can better monitor and manage complications that may arise, consequently reducing late maternal deaths and improving overall maternal health outcomes.
Innovations Needed in Maternal Healthcare Services
Investing in innovations within maternal healthcare services is crucial for reversing the troubling trends in maternal mortality. Technologies such as telemedicine can improve access to care for expectant mothers, especially in underserved areas where traditional healthcare options may be limited. By leveraging digital health solutions to provide remote consultations and ongoing monitoring, healthcare providers can enhance their support for pregnant individuals throughout their journey.
In addition to technological advancements, the integration of community-based programs can empower women by providing them with resources and information needed for making informed health decisions. Support groups, educational workshops, and advocacy initiatives can create a more supportive environment for mothers, improving their experience as they navigate the complexities of pregnancy and postpartum care. Building a robust infrastructure that fosters innovation in healthcare delivery will be essential for reducing maternal mortality rates.
The Role of Public Health Infrastructure in Maternal Health
The public health infrastructure in the United States plays a pivotal role in addressing maternal mortality. By ensuring comprehensive tracking and reporting of maternal health data, public health systems can identify trends, allocate resources effectively, and implement necessary interventions aimed at reducing maternal mortality rates. Unfortunately, the current public health infrastructure has been under threat due to budget cuts and deprioritized funding for maternal health initiatives.
To ensure progress in maternal health outcomes, there must be a renewed focus on strengthening public health infrastructure. This includes advocating for increased funding, expanding data collection efforts, and fostering collaboration between healthcare providers and community organizations. A robust public health framework will empower stakeholders to develop and implement innovative solutions that holistically address the challenges surrounding maternal mortality and improve health equity.
Empowering Women Through Education and Awareness
Educating women about maternal health issues is a critical strategy for reducing maternal mortality rates. Awareness of the signs and symptoms of pregnancy-related complications can empower women to seek timely medical attention, ultimately saving lives. Educational campaigns that target both expectant mothers and healthcare providers can foster a proactive approach in managing maternal health during and after pregnancy.
Additionally, community outreach programs can help bridge the knowledge gap in underserved populations. By equipping women with the necessary information about their health and available resources, these initiatives can encourage them to take an active role in their maternal care. Enhancing education and awareness around maternal health is vital for creating a culture where women feel supported and informed throughout their pregnancy journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. include cardiovascular disease, which accounts for over 20% of these deaths. Other significant contributors are hemorrhage, hypertension, and complications related to conditions such as pre-eclampsia and stroke. Addressing these causes is vital to reduce maternal mortality rates.
How have maternal health disparities affected pregnancy-related deaths?
Maternal health disparities significantly affect pregnancy-related deaths, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest mortality rates—nearly four times that of white women. These disparities highlight systemic issues in healthcare access and quality that need to be addressed to lower maternal mortality rates across all racial and ethnic groups.
What role does postpartum care play in preventing maternal mortality?
Postpartum care is crucial for preventing maternal mortality, particularly as nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur after the first 42 days post-birth. High-quality, extended postpartum care supports recovery and management of chronic conditions, which can lead to improved maternal health outcomes and reduced pregnancy-related deaths.
How significant is the rise in U.S. maternal mortality rates from 2018 to 2022?
The rise in U.S. maternal mortality rates from 2018 to 2022 is significant, increasing from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births. This uptick reflects ongoing challenges in maternal health care and highlights the need for enhanced focus on interventions to decrease preventable pregnancy deaths.
Why are late maternal deaths important in discussions about maternal mortality rates?
Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and one year after delivery, are vital in discussions about maternal mortality rates because they represent a significant portion of pregnancy-related deaths. Recognizing this timeframe encourages a more comprehensive approach to maternal health, emphasizing the importance of continuous care and monitoring during the postpartum period.
What strategies can be implemented to reduce preventable pregnancy deaths?
To reduce preventable pregnancy deaths, strategies should include improved access to quality prenatal care, enhanced training for healthcare providers, and strengthened public health infrastructure. There should also be a focus on addressing maternal health disparities and investing in innovative solutions that span from pregnancy to the extended postpartum period.
How does the COVID-19 pandemic influence maternal mortality rates?
The COVID-19 pandemic has likely exacerbated maternal mortality rates, with increased stress on healthcare systems and access to care during pregnancy and postpartum. The research indicates a significant spike in mortality rates during the pandemic, underscoring the need for resilient and equitable healthcare strategies to safeguard maternal health.
What are the challenges in tracking maternal mortality in the U.S.?
A significant challenge in tracking maternal mortality in the U.S. has been the lack of a consistent national system until 2018. The introduction of a checkbox for pregnancy on death certificates improved data collection, but many states still face issues in accurately reporting and analyzing maternal deaths, hindering efforts to understand and address the factors contributing to high maternal mortality rates.
| Key Points |
|---|
| More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income countries, worsening from 2018 to 2022. |
| 2021 saw the sharpest increase in maternal mortality rates, influenced by COVID-19. |
| Disparities exist in maternal mortality rates by race and ethnicity, with American Indian women experiencing the highest rates. |
| Cardiovascular disease, accounting for over 20% of deaths, has become the leading cause of maternal mortality. |
| Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum, are significant yet often overlooked in statistics. |
| Investment in public health infrastructure and innovative care solutions is crucial to reduce maternal mortality rates. |
Summary
Maternal mortality rates continue to be a serious concern in the U.S., where the latest research underscores a troubling trend of preventable deaths. Despite 80% of these deaths being avoidable, the nation leads high-income countries in maternal mortality, with recent data highlighting an alarming increase between 2018 and 2022. Disparities based on race and state further complicate the issue, demanding urgent attention to healthcare practices and public policy. Moving forward, a focused investment in comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care is essential to address the high rates of maternal mortality and improve health outcomes for all women.