Suicide Prevention for Older Adults: An Urgent Call to Action
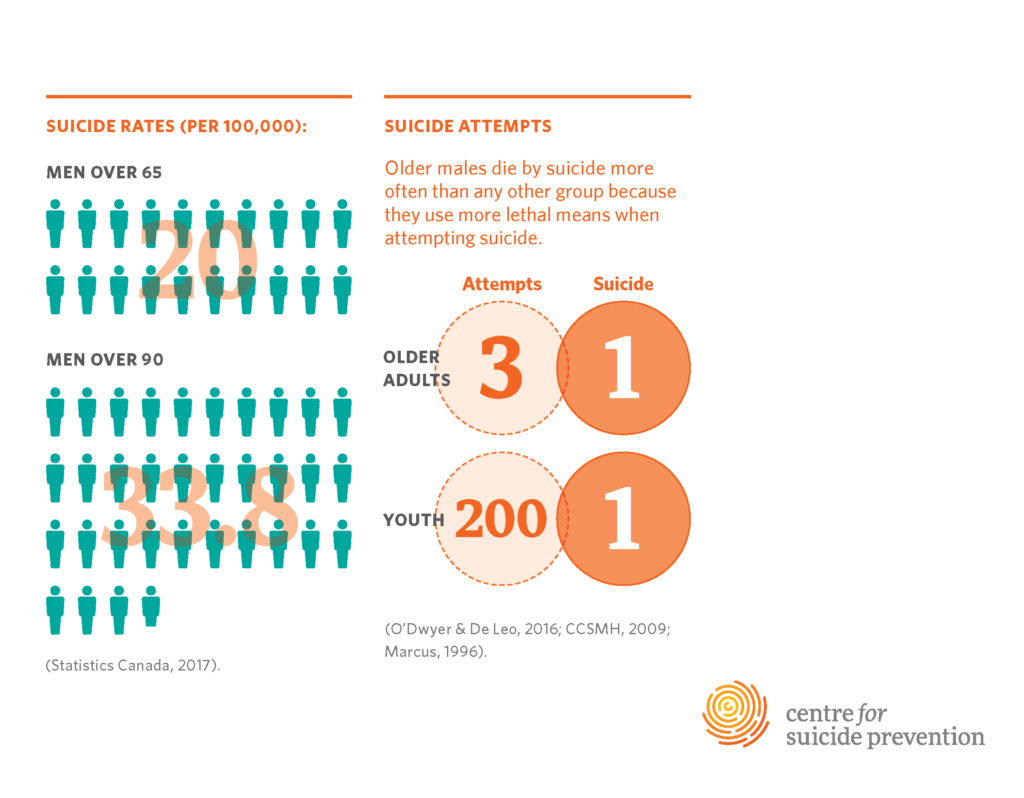
Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent and often overlooked issue that bears significant implications for society. With older adults aged 75 and above showing the highest suicide rates among all age groups, it is essential to address this critical aspect of elderly mental health support adequately. Unfortunately, many mental health resources for seniors are not easily accessible, leaving a substantial gap in support for those most vulnerable. Research indicates that numerous older adults experience isolation and despair, compounding their risk for suicidal thoughts and actions. To effectively combat the alarming trends in suicide risk in older adults, we must prioritize preventing suicide in seniors through tailored initiatives and enhance awareness about available resources.
Addressing mental health crises among senior citizens requires an understanding of geriatric suicide prevention mechanisms that cater specifically to this demographic. As societal conversations shift towards supporting the aging population, many are discovering the importance of developing strategies that focus on enhancing emotional well-being. The challenges faced by older individuals often include social isolation and a lack of tailored mental health services. By fostering a robust support system and increasing the visibility of elderly mental health resources, we can mitigate the alarming rates of suicide and provide more targeted help for those in need. Ultimately, the focus on preserving the dignity and mental wellness of our seniors is not just a moral obligation but a societal necessity.
The Mental Health Crisis Among Older Adults
Older adults face a significant mental health crisis, with rising rates of depression and anxiety exacerbated by isolation and health declines. According to recent studies, particularly adults aged 75 and older experience the highest instances of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, which necessitates a critical examination of their mental health support systems. The correlation between aging and mental health issues often goes unnoticed, leading to an alarming gap in the resources available to this demographic. Thus, addressing the mental health needs of seniors requires urgent attention from both public health officials and community-based organizations.
The stigma associated with seeking help often prevents older adults from accessing the mental health resources available to them. Families and caregivers must be equipped to recognize the signs of distress in elderly loved ones, encouraging open dialogue and professional intervention as needed. By fostering an environment that prioritizes mental well-being and by promoting targeted mental health education, society can begin to tackle the misconceptions surrounding mental health in older adults. Understanding that seniors are not simply ‘over the hill’ but rather capable individuals facing unique challenges is crucial for implementing effective change.
Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
Suicide prevention for older adults is a pressing public health issue, given the consistently high rates of suicide within this age group. Key factors such as chronic illness, loss of loved ones, and vulnerability to mental health issues amplify the risk of suicide among seniors. Geriatric suicide prevention initiatives must specifically address these challenges, advocating for customized approaches that respect the dignity and individual circumstances of older adults. This involves fostering community support networks, enhancing access to mental health services, and promoting awareness campaigns that resonate with the elderly population.
While national suicide prevention organizations have made strides in addressing suicide across various demographics, there remains a significant shortfall in resources specifically designed for older adults. Increased collaboration between healthcare providers, mental health practitioners, and community organizations can create comprehensive strategies to aid this vulnerable group. By focusing on prevention through education and outreach programs, stakeholders can ensure that effective support mechanisms are in place, ultimately saving lives and improving the overall mental health landscape for older adults.
Furthermore, initiating public policy reforms that prioritize the mental health needs of seniors will play a crucial role in suicide prevention efforts. This includes advocating for better funding of geriatric mental health programs, conducting research to understand the specific needs of older adults, and ensuring that policymakers recognize the unique challenges they face. Prioritizing older adults in the national suicide prevention strategy is not just a moral obligation but a necessary step towards safeguarding a demographic that warrants dedicated attention and compassion.
Understanding the Warning Signs of Suicide Risk in Older Adults
Recognizing the warning signs of suicide risk in older adults is essential for effective intervention. Many older individuals may exhibit depressive symptoms, withdrawal from social activities, and changes in eating or sleeping patterns that indicate significant distress. Additionally, talking about feeling hopeless or being a burden can be direct indicators of suicidal ideation. Families, caregivers, and friends should be vigilant and proactive in understanding these signs, providing emotional support and encouraging older loved ones to seek professional help when necessary.
Moreover, awareness of these warning signs can empower communities to establish tailored outreach programs. Educational initiatives aimed at family members and caregivers can help them identify and respond to signs of mental health struggles before they escalate to suicidal thoughts. Community workshops and training can also equip professionals and volunteers working with elderly populations to effectively communicate and intervene when these signs are present. Establishing a culture of vigilance and proactive care can significantly decrease the incidence of suicide among older adults.
Empowering Seniors Through Mental Health Resources
Empowering seniors through mental health resources involves creating and promoting accessible information that addresses their specific mental health needs. Mental health resources for seniors should include community programs, online platforms, and tailored support groups that ultimately encourage engagement and facilitation of conversations regarding mental well-being. When older adults can access resources that resonate with their understanding and relate to their experiences, they are more likely to seek help and support. Therefore, initiatives must prioritize making these resources simple to find and easy to use.
Furthermore, partnerships between organizations focusing on elderly mental health support and local communities can enhance the distribution of valuable information and resources. Workshops and informational sessions led by mental health professionals can help demystify mental health issues for this population, promote understanding, and reduce stigma surrounding mental health care. Initiatives such as peer support networks can further empower older adults by fostering connections among one another, enabling them to share their experiences and collectively seek help.
The Role of Family in Preventing Suicide in Seniors
Family plays a pivotal role in preventing suicide in seniors, serving as the frontline defenders against mental health decline. Often, family members can identify changes in behavior that may indicate a need for professional support. Open lines of communication can create an environment where older adults feel comfortable expressing their feelings and concerns. Thus, educating family members about the mental health challenges facing seniors can empower them to take proactive steps in supporting their loved ones.
Additionally, families can help reduce feelings of isolation and loneliness, which are significant risk factors for suicide in older adults. Encouraging social interaction, engaging in shared activities, and being present can mitigate feelings of worthlessness or despair. By fostering an emotionally supportive home life and actively involving mental health professionals when necessary, families can play an instrumental role in safeguarding the mental health and well-being of their older relatives.
Creating Age-Friendly Communities for Mental Health Support
Creating age-friendly communities is essential for providing mental health support to older adults. Communities should focus on building environments that are accessible, safe, and supportive of the unique needs of the elderly population. This includes providing easily navigable public spaces, promoting access to essential services, and facilitating transportation options for seniors to attend mental health appointments or community events. By prioritizing the design of age-friendly spaces, we can help bridge the gap in mental health support for older adults.
Furthermore, age-friendly initiatives can extend to outreach programs that connect older adults with mental health resources. Local governments and organizations can collaborate to establish programs that offer social activities, workshops, and mental health education tailored specifically for seniors. Encouraging seniors to participate in these programs can enhance their sense of belonging and purpose while simultaneously providing essential mental health support. Through collaboration and community commitment, age-friendly initiatives can cultivate a supportive environment that prioritizes the mental well-being of older adults.
The Impact of Social Isolation on Elderly Mental Health
Social isolation profoundly impacts elderly mental health, contributing to feelings of loneliness and depression that elevate the risk of suicide in older adults. As friends and family members pass away, and physical limitations prevent them from engaging in social activities, many seniors are left feeling disconnected. This isolation is compounded by the changes in their daily routines and lifestyles, which can significantly impact their mental well-being. Thus, addressing social isolation through community engagement and connection opportunities is paramount for improving the mental health landscape for seniors.
Combating social isolation requires dedication from both community members and local organizations. Initiatives such as meal delivery programs, senior centers, and connectivity through technology can foster social connections. Moreover, promoting volunteer opportunities that allow seniors to give back to their communities can establish a sense of purpose and belonging. By working actively to reduce social isolation and enhance support systems, communities can play a crucial role in improving the mental health of older adults and mitigating suicide risks.
Improving Access to Geriatric Suicide Prevention Programs
Improving access to geriatric suicide prevention programs is essential to address the growing mental health crisis among older adults. Many seniors face barriers, including transportation issues, a lack of internet access, and unfamiliarity with available resources that prevent them from seeking help. Developing programs that are easy to access and understand is crucial for ensuring that mental health support reaches those who need it most. Community-based solutions, such as mobile mental health units, can deliver services directly to elderly individuals in their homes or local gathering spaces.
Additionally, it is essential to tailor prevention programs specifically to the elderly, addressing their unique cultural and social needs. By involving older adults in the development and implementation of these programs, organizations can create more relevant and relatable mental health resources. Training healthcare providers to recognize and manage the specific mental health needs of older adults can also enhance the effectiveness of prevention strategies, ultimately reducing suicide risk and fostering healthier communities.
The Importance of Continued Research in Elderly Mental Health
Continued research in elderly mental health is crucial for understanding the unique challenges faced by older adults and developing effective interventions. As the population ages, understanding the complexities related to aging and mental health will enable policymakers to create tailored programs that prioritize the needs of this demographic. Long-term studies can identify trends, risk factors, and effective support strategies that protect the mental health of older adults. Enhanced research efforts may also contribute to the development of new resources that specifically target the nuances of geriatric mental health and suicide prevention.
Moreover, engaging older adults in the research process can help ensure that the studies reflect their lived experiences and concerns. Gathering input directly from seniors about their challenges can lead to more effective and empathetic solutions. By prioritizing funding for research focused on mental health in older adults, stakeholders can lead the way in creating targeted interventions that promote well-being and significantly reduce suicide rates within this vulnerable population.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some mental health resources for seniors focused on suicide prevention for older adults?
Mental health resources for seniors concentrating on suicide prevention for older adults include specialized hotlines like the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline (1-800-273-TALK) and resources provided by local geriatric mental health clinics. Additionally, online platforms like the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention and the Suicide Prevention Resource Center offer tailored information specifically aimed at older adults.
Why is geriatric suicide prevention crucial for elderly populations?
Geriatric suicide prevention is crucial for elderly populations due to their increased vulnerability to mental health issues such as depression and loneliness, which elevate the risk of suicide. Studies suggest that adults aged 75 and older experience one of the highest rates of suicide, making it essential to implement targeted prevention strategies and support programs that cater to their specific needs.
How can we reduce the suicide risk in older adults?
Reducing suicide risk in older adults can be achieved through a combination of increased awareness, accessible mental health services, and community support programs. Encouraging social engagement, providing targeted mental health resources, and fostering a supportive environment for discussing mental health issues are all critical components of effective prevention strategies.
What role does elderly mental health support play in preventing suicide?
Elderly mental health support plays a vital role in preventing suicide by providing older adults with the necessary tools and resources to manage mental health challenges effectively. Access to counseling, therapy, and support groups can create a sense of community and belonging, thereby decreasing feelings of isolation and loneliness that often contribute to suicidal thoughts.
What are effective strategies for preventing suicide in seniors?
Effective strategies for preventing suicide in seniors include implementing community awareness programs, improving access to geriatric mental health services, and fostering connections among seniors through social activities. Additionally, training for healthcare providers on how to recognize signs of distress and engage older patients in conversations about mental wellness is crucial.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Elderly Suicide Risk | Older adults (75+) have the highest suicide rates among age groups. |
| Lack of Resources | National organizations do not provide accessible resources for older adults. |
| Study Findings | Research from McLean Hospital underscored the need for targeted suicide prevention for older adults. |
| Internet Usage | Older adults increasingly seek health information online but struggle to find help for suicide prevention. |
| Campaign Effectiveness | Public-facing initiatives have been effective, but lack focus on older adults. |
| Call for Action | There is a need for tailored resources and increased funding for older adult suicide prevention. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue that demands immediate attention. As this population faces the highest rates of suicide, it is imperative that effective resources be made available and easily accessible. The disturbing findings from recent studies highlight significant gaps in support systems currently in place, emphasizing the urgent need for improved online resources tailored for older adults. By addressing these disparities and implementing targeted prevention strategies, we can work towards safeguarding the mental health and well-being of our older population.